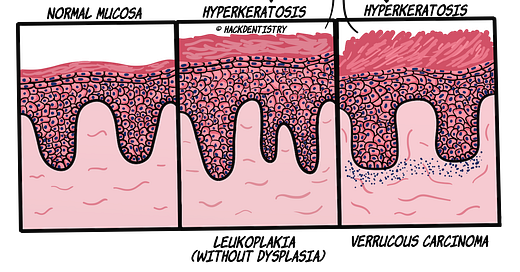
Common histopathology terms - Hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is an increase in the corneal layer or stratum corneum. Usually in epithelial lesions (especially white lesions), there is hyperkeratosis accompanying hyperplasia of the epithelium.
Hyperkeratosis could be described as being
Hyperorthokeratotic --> increase in orthokeratin (corneal layer)
Hyperparakeratotic --> increase in parakeratin (corneal layer)
The difference between orthokeratin and parakeratin is that parakeratin would show pyknotic nuclei and orthokeratin would not.
Examples of lesions manifesting hyperkeratosis 👉 white lesions like
leukoplakia,
verrucous carcinoma,
verrucous hyperplasia,
tobacco pouch keratosis,
nicotine stomatitis,
frictional keratosis (cheek, tongue, lips and alveolar ridges).
💡KNOW THY FACTS!
Leukoplakia or other white lesions for that matter, appear white because of the thickened surface keratin layer and the hyperplastic epithelium. This thickened abnormal keratin layer evenly reflects the visible light spectrum (as opposed to being permeable to visible light and the red spectrum being reflected by the connective tissue). This clinically masks the vascularity (redness) of the underlying connective tissue making it appear white!💰"Christmas discount sale"
You could use the coupon code
“hd20discount”
to avail a discount of 20% for the 6 months and 12 months subscription plans on all course bundles.
Offer ends at the end of 31st December.