What is Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia (PVL)?
Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia(PVL) is rare high risk form of leukoplakia first described by Hansen and associates in 1985.
This lesion is deceptive in that, it manifests as an unsuspicious, homogenous white lesion in the early stages and does not show alarming features when biopsied.
However, the problem begins when the lesion starts to slowly spread to other areas of the oral cavity.
Clinical Features
The lesion becomes diffuse and multifocal, either confluent or isolated and surface of the lesion develops wart like projections to become verrucous. They may also have red areas interspersed in between.
Other features identified as characteristic are
its predisposition in women(4:1) and older patients (mean age of 60),
lack of risk factors and
its predominant occurrence at the buccal mucosa and tongue, though few other studies consider the keratinized sites, gingiva and alveolar ridge to be most frequently affected.
Histopathology
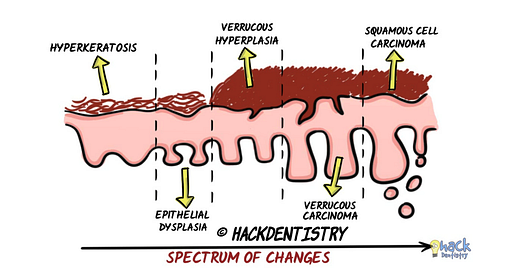
Microscopy may show a spectrum of changes depending on what stage the lesion is biopsied.
It may range from a simple hyperkeratosis initially to epithelial dysplasia, verrucous hyperplasia, verrucous carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
Prognosis
PVL has a malignant transformation rate of 70-100% and is persistent, irreversible and resistant to all forms of treatment with a high recurrence rate.